 The global automotive market has seen tremendous growth since 2010 recording a Year on Year (YoY) growth of 3.9 percent in 2013 compared to 2012; to approximately 83.5 million vehicles and is expected to grow to 107.9 million vehicles by 2020. Asian markets are likely to lead the growth in Passenger Vehicle (PV) production accounting for 44 percent of global automotive sales. Small hatchbacks are expected to account for 55 percent of total sales and compact vehicles priced at $10,000–$15,000 are expected to be an attractive market in developed economies, with a share of about 21 percent. Cars are also expected to shift from traditional sizes (more than 3,500 mm length) to Micro-cars with less than 3,500 mm length.
The global automotive market has seen tremendous growth since 2010 recording a Year on Year (YoY) growth of 3.9 percent in 2013 compared to 2012; to approximately 83.5 million vehicles and is expected to grow to 107.9 million vehicles by 2020. Asian markets are likely to lead the growth in Passenger Vehicle (PV) production accounting for 44 percent of global automotive sales. Small hatchbacks are expected to account for 55 percent of total sales and compact vehicles priced at $10,000–$15,000 are expected to be an attractive market in developed economies, with a share of about 21 percent. Cars are also expected to shift from traditional sizes (more than 3,500 mm length) to Micro-cars with less than 3,500 mm length.
With the tech savvy Gen Y, that is, people born between mid-1970s and mid-1990s, vehicle technology will become more connected and will also become a part of the ‘Internet of Things’, (uniquely identifiable objects and their virtual representations in an Internetlike structure). As more and more intelligent vehicles are introduced with technologies like 3G/ Wi-Fi connectivity, Internet radio, Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) communication, comfort and safety features, which will make vehicular travel less cumbersome will be brought in.
Powertrain
All major auto regulatory bodies in developed markets have established strict emission and efficiency norms and similar bodies in developing markets are hastening enforcement of such plans without hindering industrial growth. With the already strict emission regulations looking to get stricter, OEMs have taken a few steps to reduce their carbon footprint, the first of which is to downsize the engine while maintaining power output, by application of technologies such as Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI), Variable Valve Timing (VVT), and Turbocharging.
OEMs have switched to lighter materials, such as aluminum, to construct their engine blocks to reduce overall weight, while motorsports and exotic vehicles have switched to magnesium. They have also moved on to more electronic controlled transmission operation systems to increase the comfort of city driving with the introduction of automatic transmissions. Due to the increased costs involved with automatics, emerging countries are expected to switch to Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT), which provides the comfort of shifting without adding much cost or weight.
With the many nations embracing the concept of ‘Innovating to Zero’, which envisages a ‘Zero Concept’ world with zero emissions, zero accidents, zero fatalities, zero defects, and zero breaches of security, vehicle designers are focusing more on electric and hybrid vehicles. A large number of hybrid concepts by all major OEMs were displayed in various auto shows in 2013. A major focus is on plug-in hybrids with full hybrids expected to become plug-in hybrids in the developed world, and 85 percent of cars in the European Union expected to have start-stop systems by 2020. These vehicles have entirely different components in their powertrain and are expected to increase the size of the components market for hybrid vehicles.
Chassis
All major OEMs have adopted aluminum space frames over the traditional ladder chassis due to weight saving and increased stiffness. This has vastly reduced weight by replacing steel with aluminum but steel is still used in many punched parts due to its formability and strength at low costs. A recent trend has been the use of advanced high strength steel to replace traditional steel components to reduce the weight by up to 20 percent at almost no extra cost.
Another trend is OEMs switching to modular designs for their platforms. This enables sharing of systems and components across model line-ups and across vehicle types, which results in an increase in components volumes while driving down costs.
With more and more customers looking for ease of driving, systems such as electric power steering are expected to become standard in all vehicles. Other technologies that are expected to increase their penetration are active steering systems and drive-by-wire systems.
Body in White
Another measure by OEMs to reduce overall weight is to use lighter plastics and polycarbonates instead of traditional materials in the interior paneling and other comfort components. OEMs have switched to the use of plastics in major components such as fuel tanks and HVAC systems. HVAC systems traditionally used steel as the primary material but are now manufactured with aluminum in the heat exchanger and plastic ducting. This replacement using plastics can save up to 50 percent in weight and the insulating nature of plastic prevents transfer of heat to the body.
A possible technology to replace automotive glass is the use of clear polycarbonates and polycarbonate-glazed glass, which are currently used in motorsports and exotic vehicles. The use of such polycarbonates can reduce weight of the transparent components by up to 50 percent but current manufacturing costs are too high for mass market use. Currently, polycarbonate plastics are used for headlight housing. A point of concern for using polycarbonates is that they do not shatter like glass and could hamper the efforts of rescue personnel in the event of an accident.
Carbon fiber and carbon fiber reinforced polymers are also employed in motorsport and exotic vehicles to add safety while reducing overall weight. This technology, like polycarbonate is currently too expensive to be used in mass market vehicles but with the increase in safety and improvement in carbon fiber manufacturing processes to reduce manufacturing costs the possibility of future vehicles featuring this is very high.
Safety
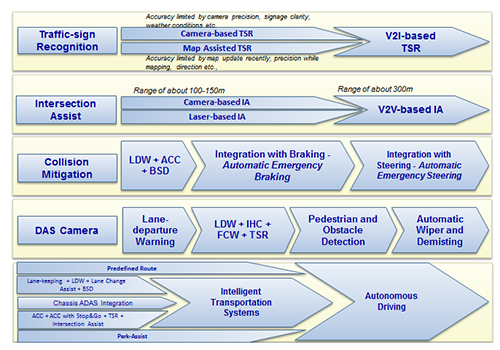
Government bodies have become very safety-oriented with increasing number of accidents on road and fatalities. With this in mind, multiple organizations are working on a slew of technologies, which can be integrated into each vehicle. With the advent of vehicleto vehicle connectivity and vehicleto-infrastructure communications (collectively referred to as V2X), safety systems will take a major leap into Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) such as collision assist, Automatic Cruise Control (ACC) and Lane Departure Warning (LDW). The various systems that are expected to be introduced are mapped with their timelines, (See iIlustration).
Most of the systems listed in illustration require complex algorithms and robust V2X communication to work as expected. Global OEMs have formed alliances and partnerships with global tech majors to integrate these systems in vehicles by 2020. Some European OEMs have already installed some of these ADAS into their high-end models and have plans to bring them into their mass models as well, to meet stricter safety regulations being imposed in developed markets.
Telematics and Infotainment
Telematics typically is any integrated use of telecommunications and informatics. GPS navigation, integrated hands-free cell phones, wireless safety communications, and automatic driving assistance systems are covered under the telematics umbrella. These technologies are being integrated into the vehicle entertainment system and hence the term “Infotainment”.
OEMs are working on two types of infotainment systems: embedded connected systems, and hybrid connected system. Embedded connected systems, which is an OEM developed system, is hardwired into the cars infotainment system and smartphones have minimal roles and hybrid connected system utilise standards like Real VNC (Virtual Network Computing) viewer and server (software development kit) SDK to host content from smartphone in car at different levels. An embedded system incurs development cost and time, and is mostly supported by dedicated application stores while hybrid systems have low development costs, take less time to market, and have solutions supported by robust standards from the computing world. Innovations in display technology, such as the use of dual-view display and 3D displays will enable these systems to pass information to the driver efficiently without affecting passenger
entertainment.
Bottom Line
With vehicle technology converging with intelligent software, there will be smarter vehicles in the future capable of autonomous driving. All advanced systems such as ADAS, ACC, etc. will require an array of sensors and cameras to work as envisaged, thereby increasing volumes of the components market.
Stricter safety norms in conjunction with emission and efficiency norms mean vehicle light-weighting is here to stay. This involves replacing heavy components made from steel and other traditional materials with lighter ones made from polycarbonates, carbon fiber, and plastics. ACI
By Automotive & Transportation Practice, Frost & Sullivan.











Pingback: Homepage